What is CNC Machining?
What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This process enables the production of precise parts by removing material from a workpiece using various cutting tools.
CNC Machining Process Steps
- Design Creation: Engineers design the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
- Programming: The design is converted into a CNC program using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, generating G-code.
- Machine Setup: Operators set up the machine, securing the workpiece and installing the appropriate tools.
- Machining: The CNC machine executes the program, performing the necessary cuts and movements.
- Quality Control: Finished parts are inspected for accuracy and quality.
Types of CNC Machining Operations
- Milling: Rotating cutting tools remove material to shape the workpiece.
- Turning: The workpiece rotates while a stationary cutting tool shapes it.
- Drilling: Creating round holes in the workpiece.
- Boring: Enlarging existing holes with precision.
- Grinding: Using an abrasive wheel to achieve fine finishes.
- Cutting: Separating material using various methods like laser or plasma cutting.
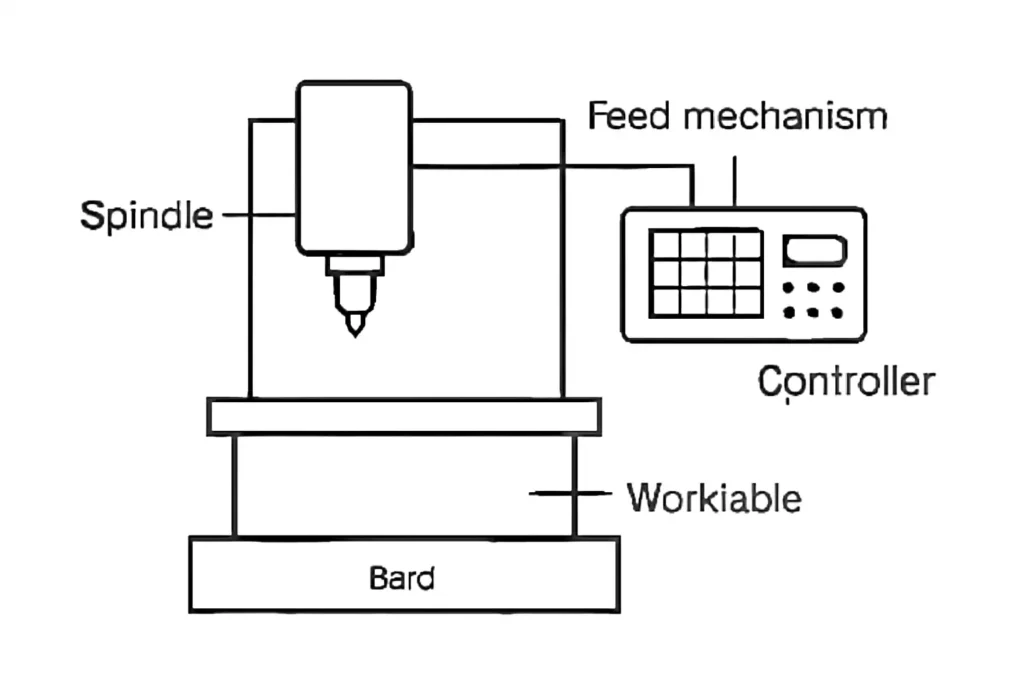
CNC Equipment and Key Components
- CNC Machine: Includes the bed, spindle, axes, and tool changer.
- Controller: The computer system that interprets G-code and controls machine movements.
- Axes: Typically X, Y, and Z axes, allowing multi-directional movement.
- Spindle: Rotates the cutting tool at various speeds.
- Tool Magazine: Stores multiple tools for automatic changing.
- Fixtures: Secure the workpiece during machining.
CNC Programming
CNC programming involves writing code (G-code and M-code) that directs the machine’s operations. G-code controls movements, while M-code manages auxiliary functions like coolant flow.
Looking for CNC machines built to handle graphite dust?
Explore Dust-Proof CNCsRecommended Machines for Graphite Machining

GraphiteCNC X1
Compact design, sealed chamber, HEPA filtration—ideal for precision graphite parts.
Learn More →
